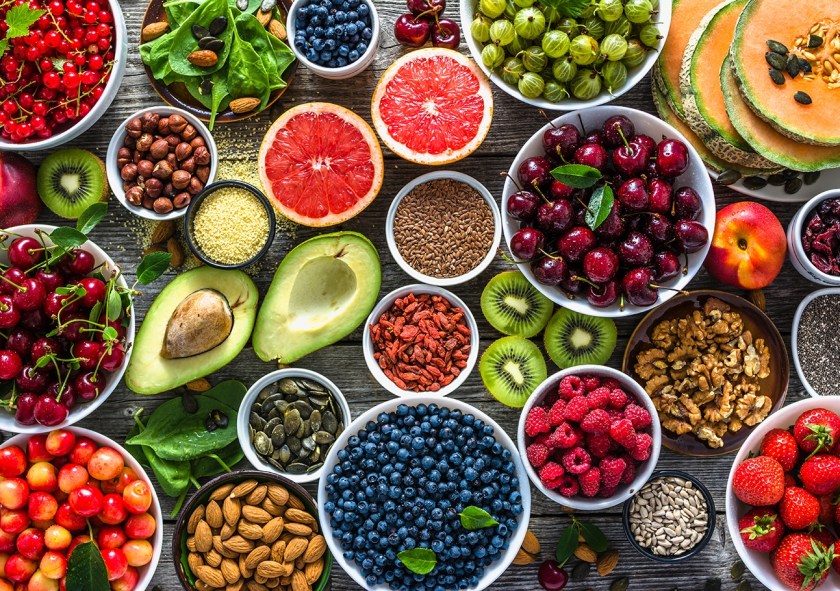
You probably include some superfoods in your meals already, but there may be room for improvement. Superfoods are nutrient-dense, whole foods packed with vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that support overall health, reduce disease risk, and boost energy. While technically a marketing term rather than a medical definition, incorporating foods like berries, leafy greens, nuts, and salmon provides significant health benefits. Here are 10 superfoods identified in a 2022 article on the Harvard Medical School Health Publishing website:
- Berries. High in fiber, berries are naturally sweet, and their rich colors mean they are high in antioxidants and disease-fighting nutrients.
- Fish. Fish can be a good source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which help prevent heart disease.
- Leafy greens. Dark, leafy greens are a good source of vitamin A, vitamin C, and calcium, as well as several phytochemicals (chemicals made by plants that have a positive effect on your health). They also add fiber into the diet.
- Nuts. Hazelnuts, walnuts, almonds, pecans — nuts are a good source of plant protein. They also contain monounsaturated fats, which may be a factor in reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Olive oil. Olive oil is a good source of vitamin E, polyphenols, and monounsaturated fatty acids, all which help reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Whole grains. A good source of both soluble and insoluble fiber, whole grains also contain several B vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients. They have been shown to lower cholesterol and protect against heart disease and diabetes.
- Yogurt. A good source of calcium and protein, yogurt also contains live cultures called probiotics. These “good bacteria” can protect the body from other, more harmful bacteria.
- Cruciferous vegetables. These include broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, collard greens, kale, kohlrabi, mustard greens, radishes, and turnips. They are an excellent source of fiber, vitamins, and phytochemicals including indoles, thiocyanates, and nitriles, which may prevent against some types of cancer.
- Legumes. This broad category includes kidney, black, red, and garbanzo beans, as well as soybeans and peas. Legumes are an excellent source of fiber, folate, and plant-based protein. Studies show they can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Tomatoes. These are high in vitamin C and lycopene, which has been shown to reduce the risk of prostate cancer.





































































You must be logged in to post a comment.